Financial Technology
Digital Finance Cube
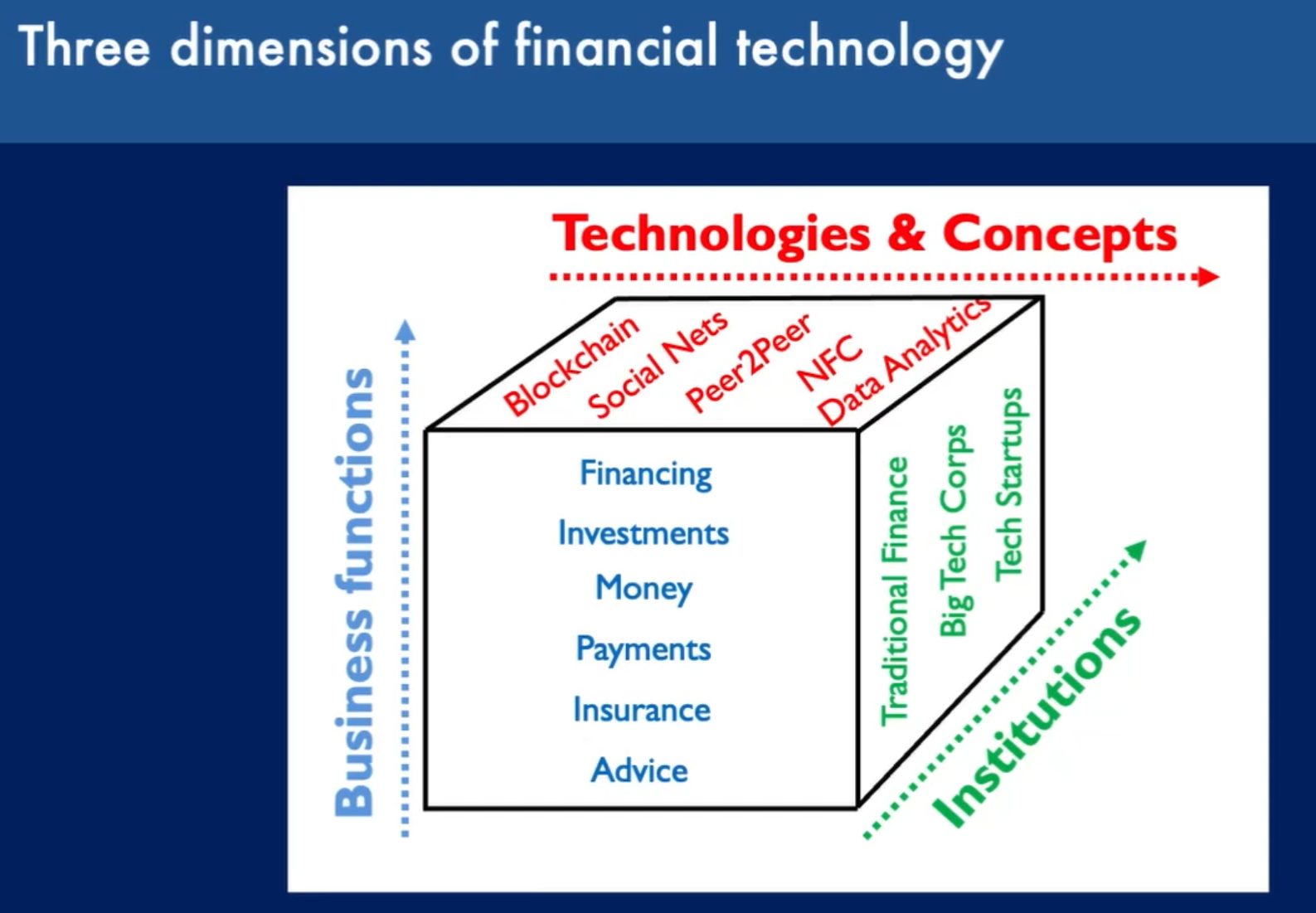 Digitalisation is a form of incremental innovation.
Digitalisation is a form of incremental innovation.
Big Tech wants to expand into financial services because it helps them perform lock-in, gives Network Effect and helps them acquire more customer data. This is commonly referred to as TechFin, vs FinTech (which is companies focusing on finance). 
FinTech/TechFin users
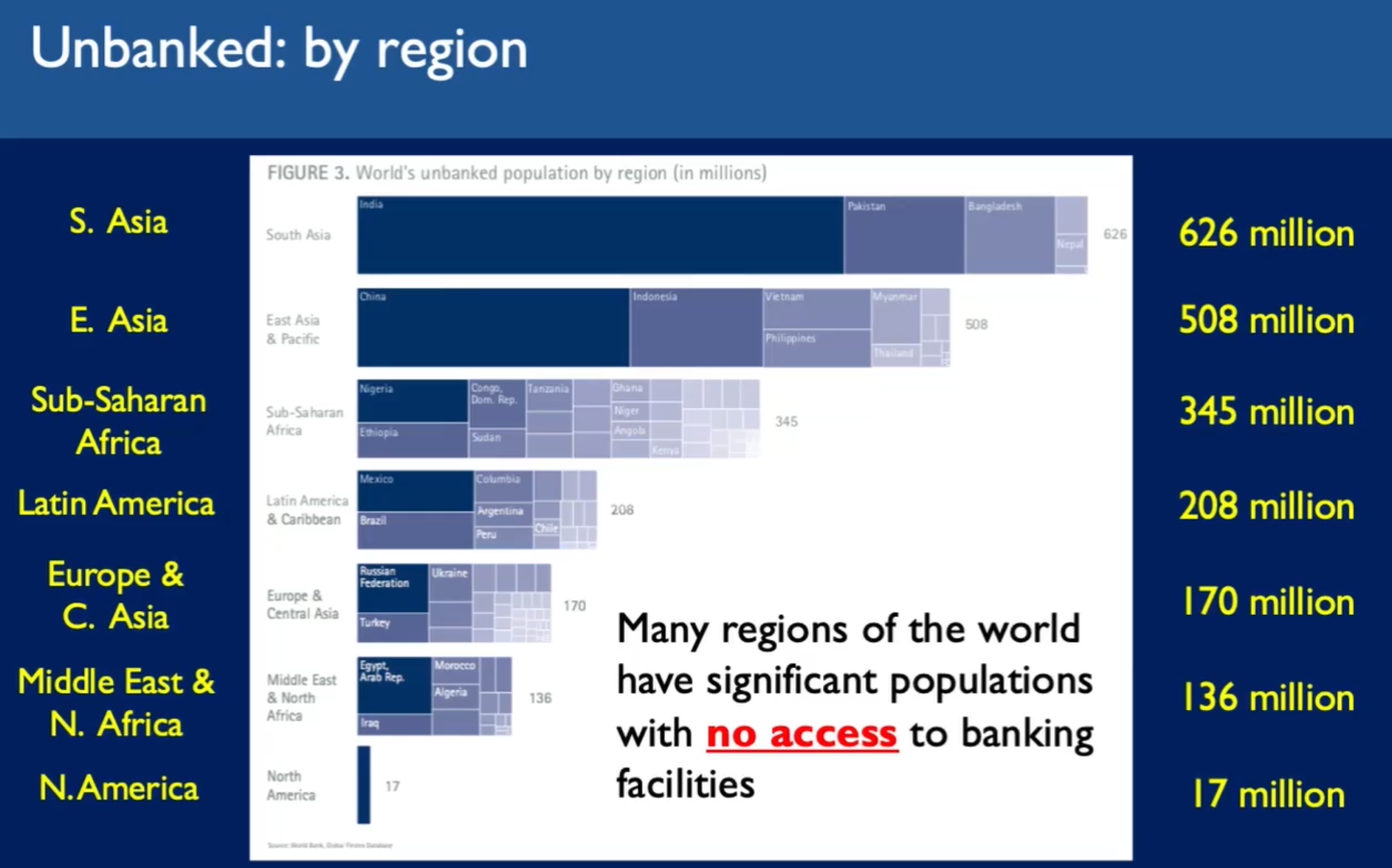
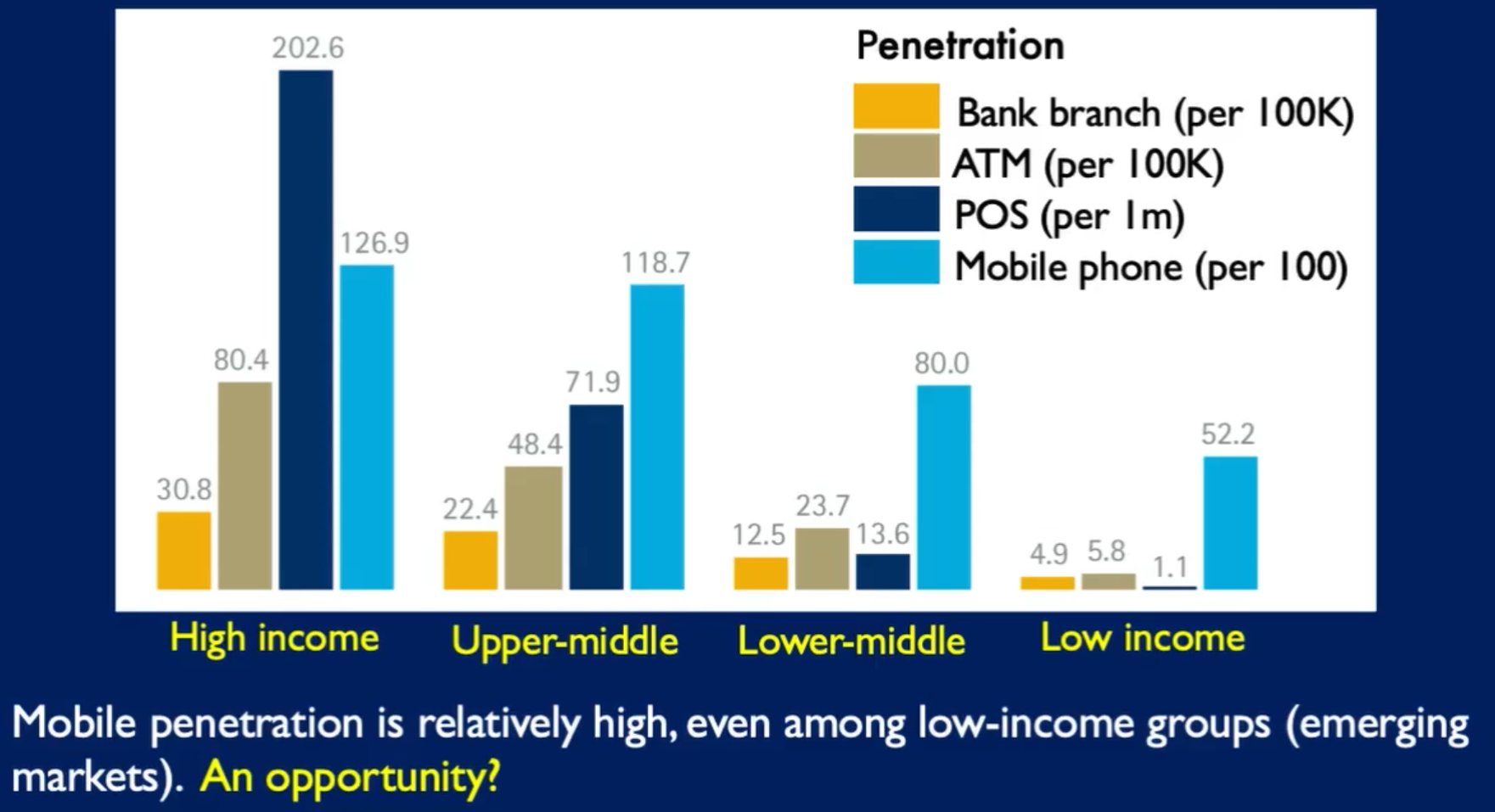
Mostly young, and wealthy - at least in countries with mature banking sectors. Almost 70% of the world population are underserved or not served at all by financial products.
The traditional banking sector did not serve the less wealthy.
Un/underbanked needs
- Easy access
- Appropriate products
- Attractive to use (low costs and incentives)
Financial Regulation
- To protect actors
- To improve efficiency
- To reduce risk by controlling what banks can use funds for
- To help build trust
Some regulators prefer to not regulate fintech/techfin at first so that progress is not delayed, while others are afraid of innovation.
China for example has been leading techfin growth through low regulation, while India has heavy regulations on financial products.
Phases of company growth
- Too small for regulators to care
- Too large to ignore
- Too big to fail (gov will bail out if needed)
LASIC principles of success
Low margin
Information services are expected to be practically free, so it’s critical to be able to sustain low margins.
Asset light
Keep fixed costs low by avoiding expensive purchases such as infra, buildings etc. Should try use existing infra where possible.
Scalable
Technology and business model must scale to reap benefits of the network effect. Scaling must not compromise costs or efficiency. Scaling must happen quickly to keep ahead of competitors.
Innovative
To encourage adoption, the product needs to be innovative, ideally a new business model.
Compliance-easy
You want to make sure regulators aren’t getting in your way, or even helping you with funding, etc. Try and avoid needing to perform KYC.
Successful Examples
TransferWise
Transfers between different currencies with low fees by not actually doing international transfers, just depositing/withdrawing from local bank accounts. It uses very little startup capital as it matches customer funds on either side. 
M-Pesa
Mobile phone based money transfer, finance, and micro-finance system. Does not need mobile data, works directly on the SMS network. Funds can be deposited/withdrawn from a large network of agents such as shopkeepers. Launched by existing telecoms network.
M-Pesa has lifted 2% of the household population of kenya out of poverty.
AliPay
Introduced in 2004 as an escrow system for Alibaba. QR codes are very popular in China for AliPay and other services. In 2018 83% of payments were made via mobile payment methods. WeChat pay and AliPay are the leaders. 
mBank
Internet only bank founded in Poland. Now fourth largest by assets. Has since expanded to other countries, and now licenses their system to other institutions. Offers unsecured personal loans. 
Cards
Q: What proportion of the world population are underserved/unserved by financial products? A: 70%
Q: What are the LASIC principles of success? A: Low margin, Asset light, Scalable, Innovative, Compliance-easy
Q: What is M-Pesa and their impact? A: SMS based money transfer. Lifted 2% of Kenya’s households out of poverty.
Q: What is an example of incremental innovation? A: Digitalisation, since it can be applied slowly in steps.
Q: What is the difference between FinTech and TechFin? A: FinTech refers to companies focusing on finance technology, whereas TechFin is existing Big Tech companies moving into finance.
Q: What countries have opposing approaches to fintech regulation? A: China is leading growth through low regulation, while India is the opposite.
Q: What are the phases of company growth w.r.t regulation? A: - Too small for regulators to care
- Too large to ignore
- Too big to fail (gov will bail out)
Q: What is TransferWise? A: Low-fee international transfers through matching customers on either side.
Q: What is AliPay? A: Originally introduced in 2004 as an escrow system for Alibaba. QR codes are very popular in China for payments.
Q: What is mBank? A: Internet-only bank founded in Poland. Has expanded to other countries and licenses their system to other institutions. Offered unsecured personal loans.